- +91-11-4044-5999
- info@cdri.world
-
Copernicus Marg, New Delhi, INDIA
Community disaster resilience assessment by integrating functionality of buildings and critical infrastructure systems
Mr Sohel Rana,
Chittagong University of Engineering & Technology (CUET), Bangladesh.
Dr Subhrajit Dutta
National Institute of Technology Silchar, India
Dr Ram Krishna Mazumder
Arcadis U.S. Inc.
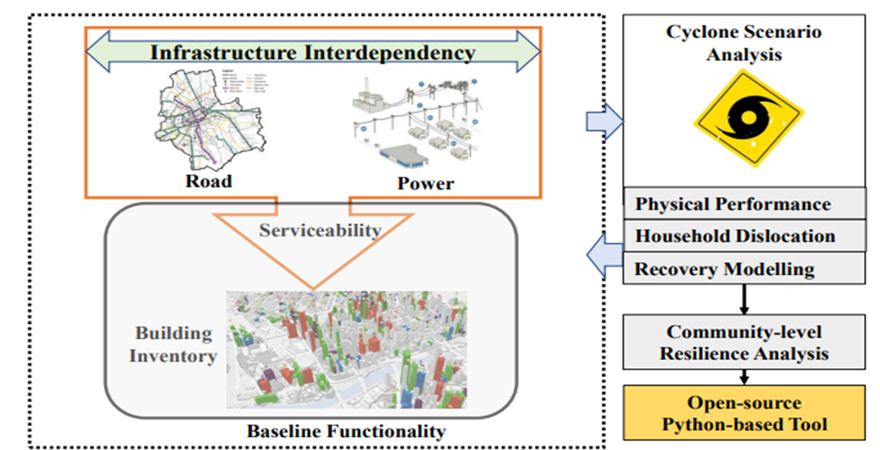
Research problem: While extensive research has been conducted on resilience analysis of interdependent critical infrastructure systems and buildings separately, research on analyzing the functionality of a community based on the combined performance of buildings and critical infrastructure systems considering climate change is rare and remains an overarching challenge and gap.
Innovation/novelty: To analyze post-disaster community resilience, the proposed approach builds the idea of evaluating the baseline functionality of buildings where a building’s structural performance is coupled with the performance of multiple interdependent infrastructure systems through scalable network graph analysis. An open-source Python-based analysis tool will also be developed.
Proposed solution: The proposed approach will focus on recovery affected by constraints, resources, and interdependency of systems. This will close gaps in functionality analysis of buildings considering infrastructure interdependency and climate change and develop an easy-to-use resilience analysis framework at a community scale, executed by developing a Python-based tool.
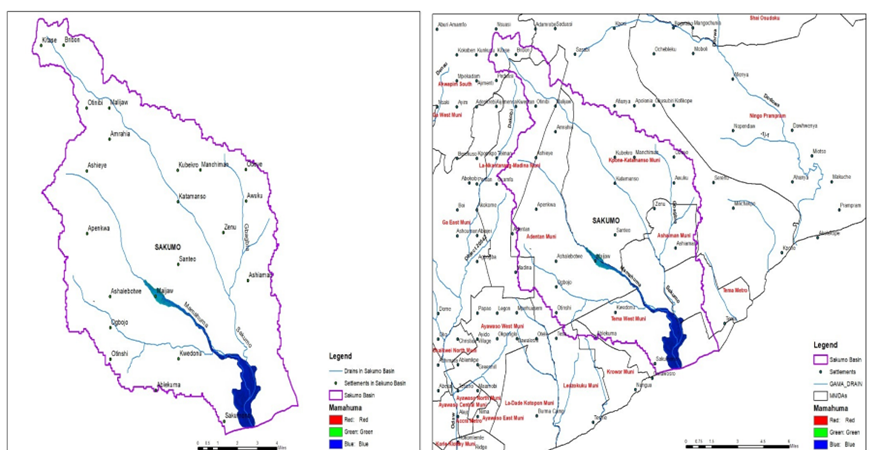
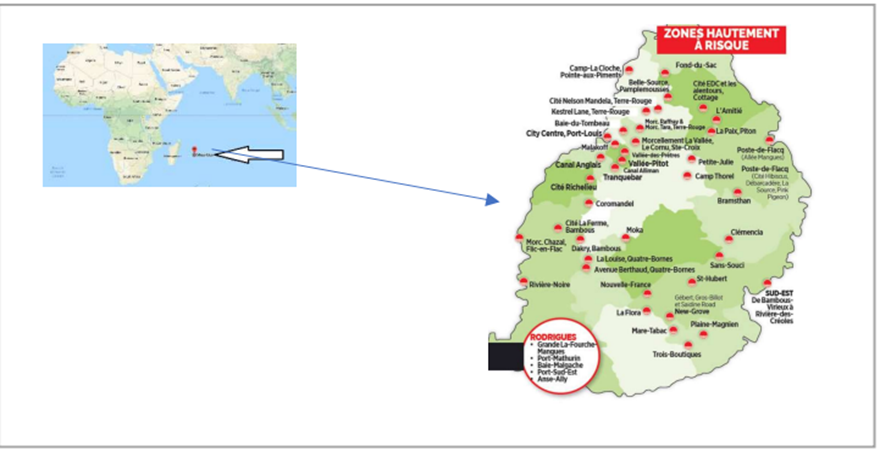
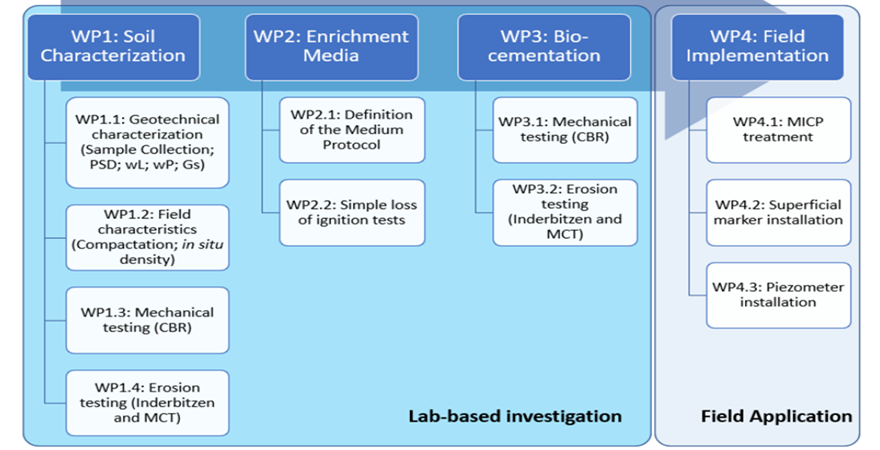
Research Methodology: The community cyclone resilience analysis framework consists of five manifolds: (1) characterizing cyclone hazard scenario; (2) analyzing physical damage to buildings and infrastructure systems; (3) assessing infrastructure interdependencies; (4) evaluating system performance of infrastructures; (5) examining baseline functionality of buildings combining structural integrity and infrastructure serviceability throughout the recovery.
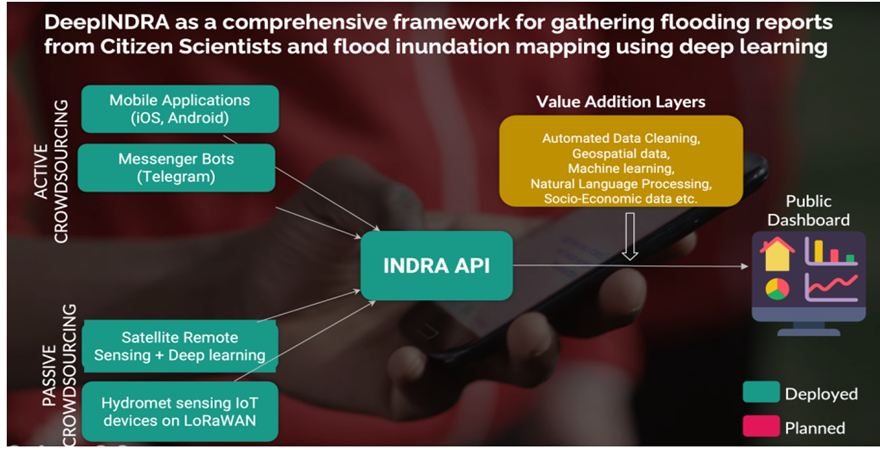
Practical application and implications: An efficient Python-based resilience analysis tool will be developed to support decision-makers in executing the proposed analysis and visualizing the results. The tool will be published on an open-source repository, such as GitHub (https://github.com/), with a user interface that real decision-makers can use without advanced training.
Assumptions It is assumed that the resilience analysis framework will apply to a general class of interconnected infrastructure systems, buildings, and any hazard type. The resilience analysis module assumes that the building will lose functionality in case of physical performance disruption or loss of essential services (e.g., water, electricity).
Scope and limitations: To adapt the proposed framework, we must engage diverse stakeholders (i.e., infrastructure operators) to identify functionality measures from a broad spectrum of existing functionality measures, particularly for infrastructure systems. However, stakeholder engagement is beyond the scope of the 12-month project but will be considered future work of the PIs.
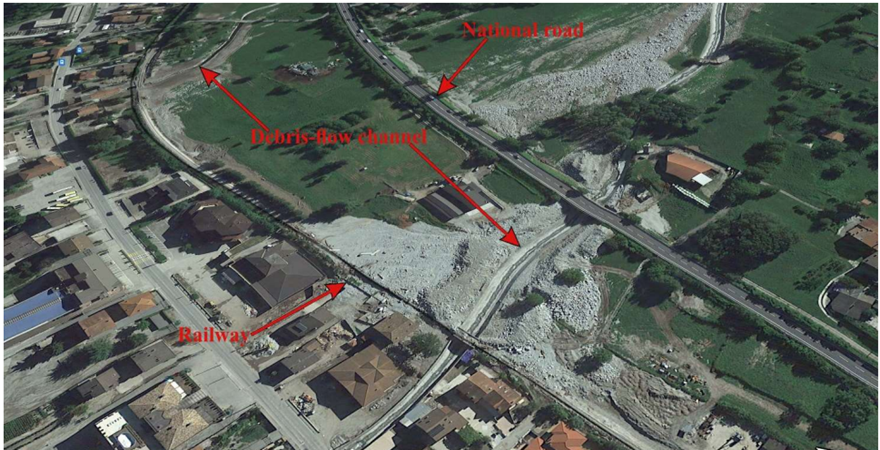
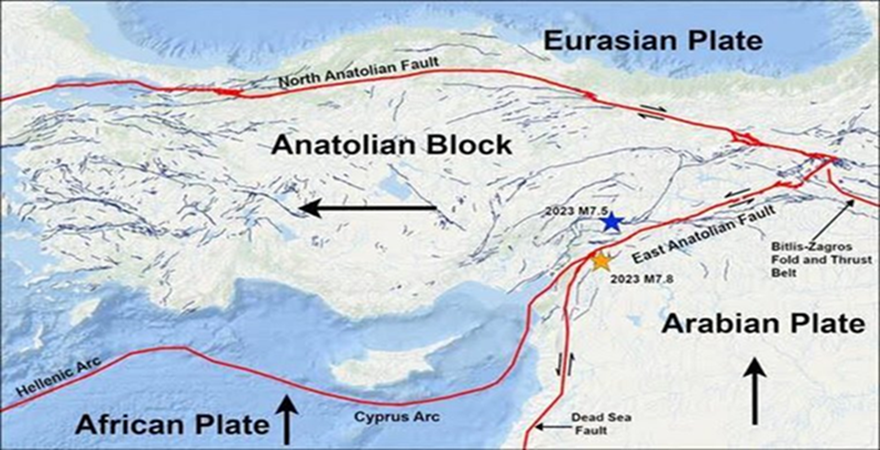
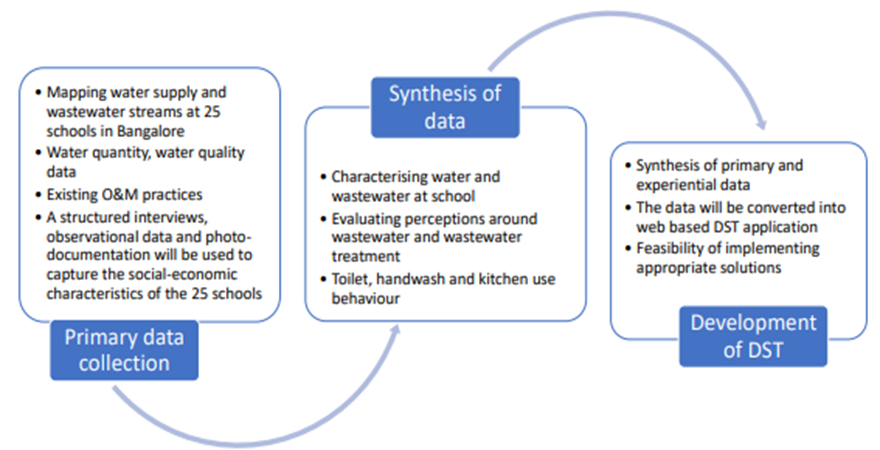
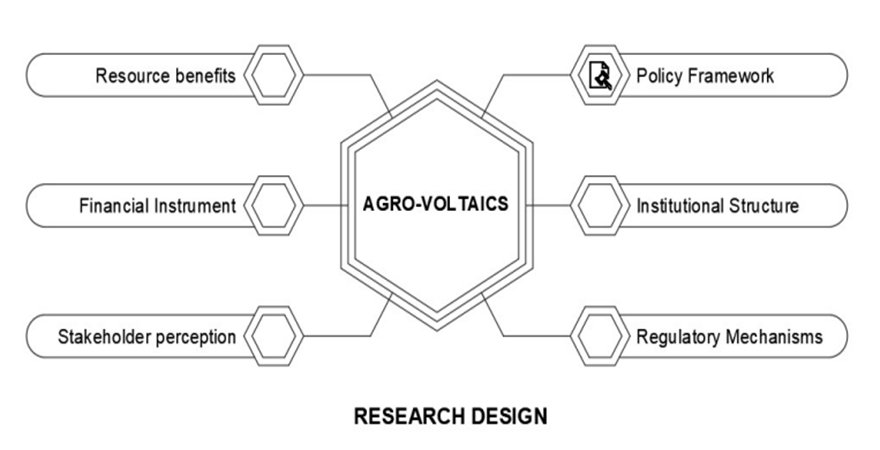
 mainstreaming inclusion of persons with disabilities in disa.png)