- +91-11-4044-5999
- info@cdri.world
-
Copernicus Marg, New Delhi, INDIA
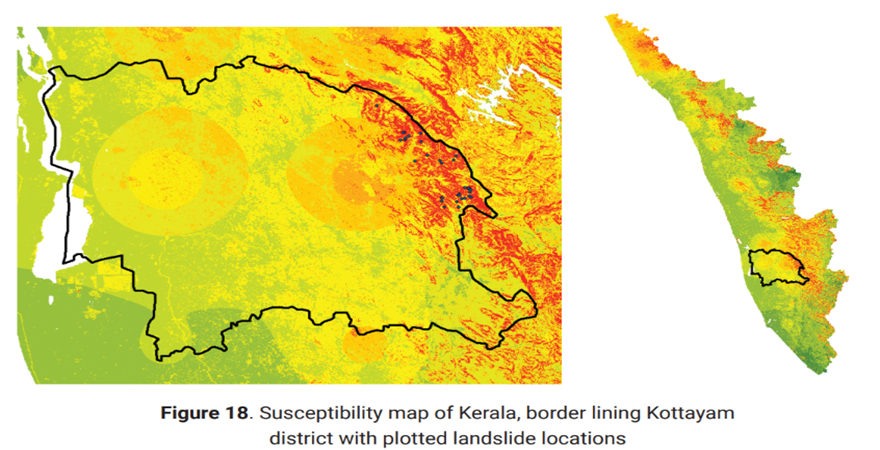
Regional road network resilience using landslide susceptibility model
Nitheesh K
Indian Institute of Technology Palakkad, India
Abhijith A
Indian Institute of Technology Palakkad, India
Dr Rakesh J Pillai
Indian Institute of Technology Palakkad, India
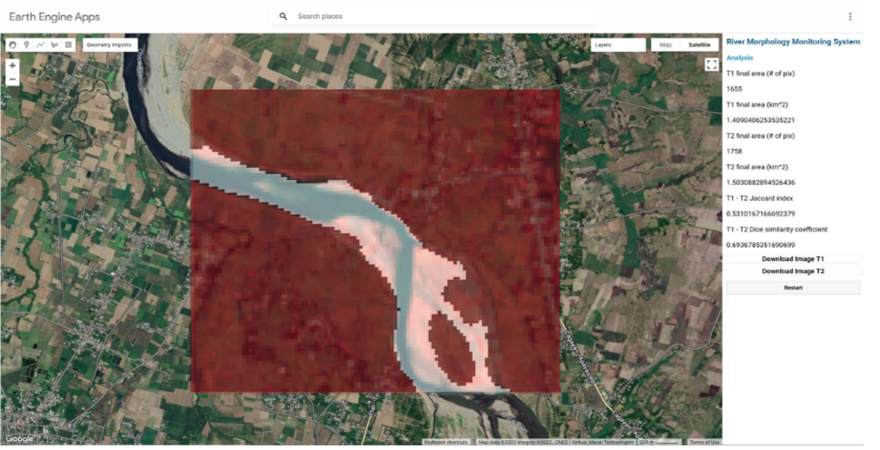
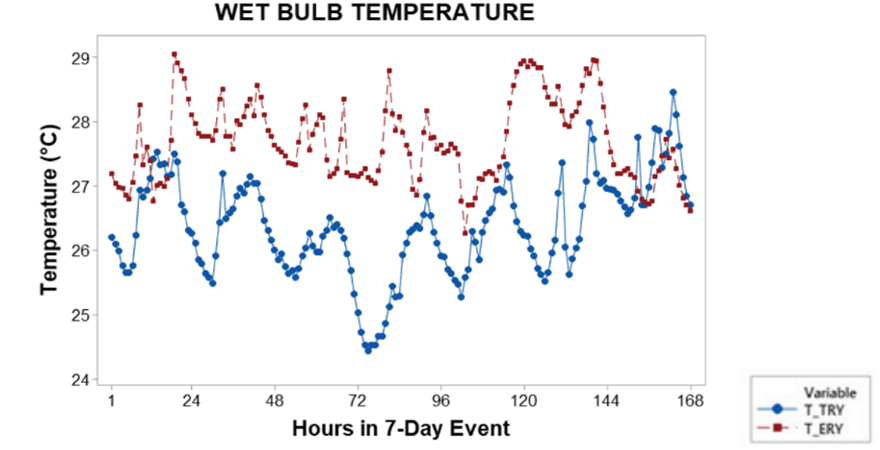
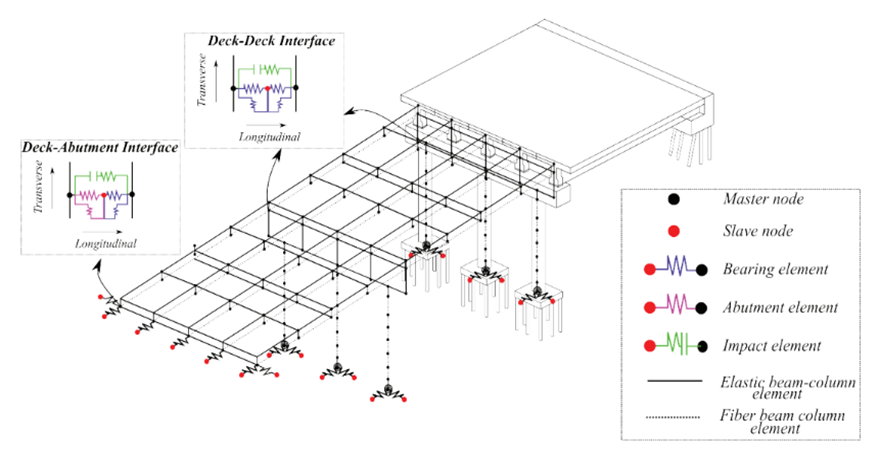
The lack of a reliable landslide susceptibility map in the Western Ghats has led to poor quantification of risk associated with rainfall-induced landslides to the road networks, as these macro-level susceptibility maps fail to consider the geotechnical characteristics of the overlying soil. The study introduces a framework to improve susceptibility mapping by performing probabilistic slope stability analysis, using different simulation techniques. In addition, optimization techniques are also incorporated, to determine the location of probe points in an optimal manner, thus improving the resilience and recovery of road networks. This would eventually lead to better mitigation plans and evacuation strategies, during such incidents.


.png)

.png)
, nepal.png)