- +91-11-4044-5999
- info@cdri.world
-
Copernicus Marg, New Delhi, INDIA
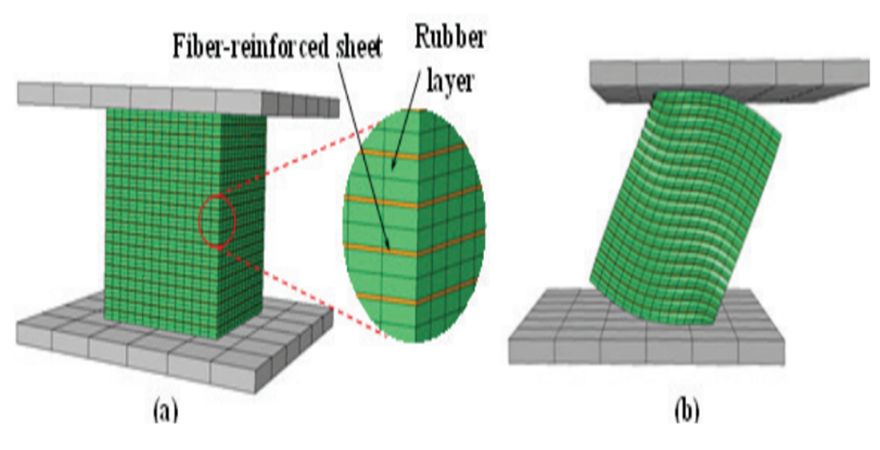
Innovative structural protection system for resilient community against multiple hazards
Prof Vasant Annasaheb Matsagar
Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Delhi, India
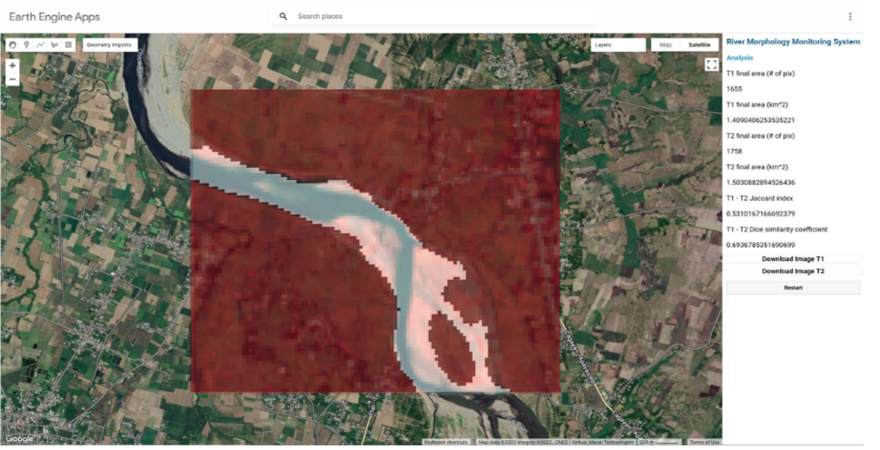
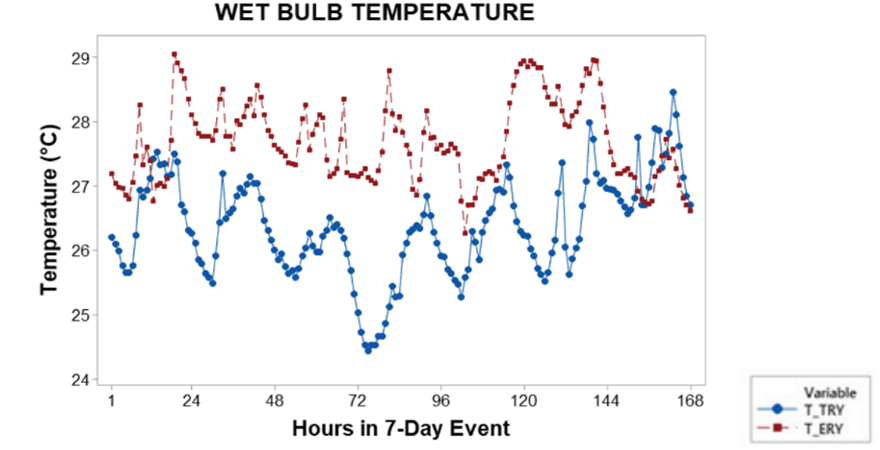
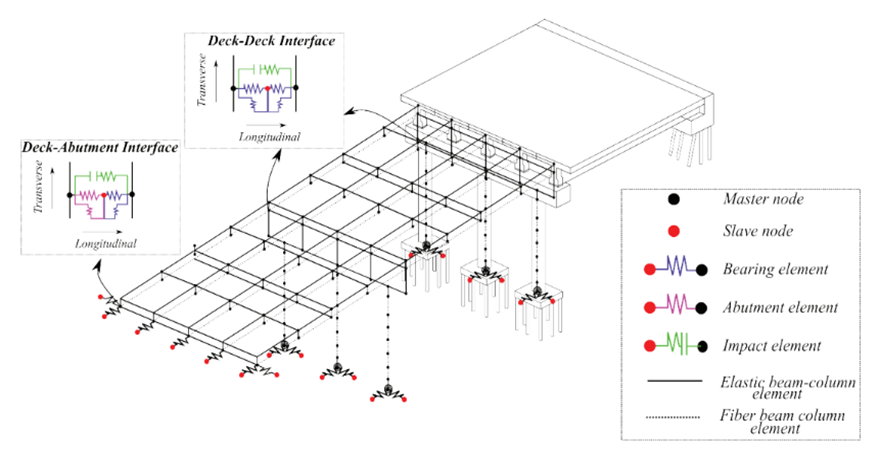
Abstract: Lifeline structures such as hospital buildings must remain functional not only during but also after any natural, accidental or humanmade disaster. Some of the major hospital buildings in India have experienced ageing, which has hampered their structural performance against excitations from earthquake and wind excitations. To improve the resilience of hospital buildings, new technologies are, therefore, required to be introduced, which must also have higher fire rating. Unfortunately, in the past several earthquake-triggered collapse of hospital buildings and fatalities caused due to fire accidents were reported. Hence, through the research work carried out under this fellowship of the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI), innovative structural protection system for resilient community against multiple hazards has been developed. Specifically, novel lightweight and fire-resistant fibre-reinforced bearings (FRBs) for retrofitting of the hospital buildings under multihazard scenarios have been designed, fabricated and tested numerically as well as experimentally against the anticipated loading scenarios. To base the investigation initially, rapid visual survey (RVS) of some of the major hospital buildings in the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi was conducted for assessment of their present in-situ structural condition. Based on the observations RVS inferences were made about the requirements of their enhancement in resilience against the three hazards: earthquake, wind and fire scenarios. Base isolation for retrofitting the hospital buildings was concluded to be the most suitable alternative, supplemented with improved fire-resistance of the isolation systems. It was followed by developing analytical force-deformation relations and implementing them in finite element (FE)-based numerical simulation. Further, such FE simulations using equivalent linearization help translate this technology in real-life applications through structural designs. For load-bearing and framed structures, new types of FRBs have been conceived, developed and designed in this CDRI Fellowship project.


.png)

.png)
, nepal.png)